Step Up Your SEO Ranking With The Latest Google Core Web Vitals Ranking Criteria

by admin
It is a known fact that Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) ranking plays a poignant role in B2B digital marketing. Businesses are always hankering to enhance their ranking algorithm using the latest SEO tricks and techniques. In continuation with the same, Google is coming up with its Core Web Vitals in May 2021 and they will become the main ranking signals for search results. Let’s find out more about these new metrics that will change the whole SEO ranking game.
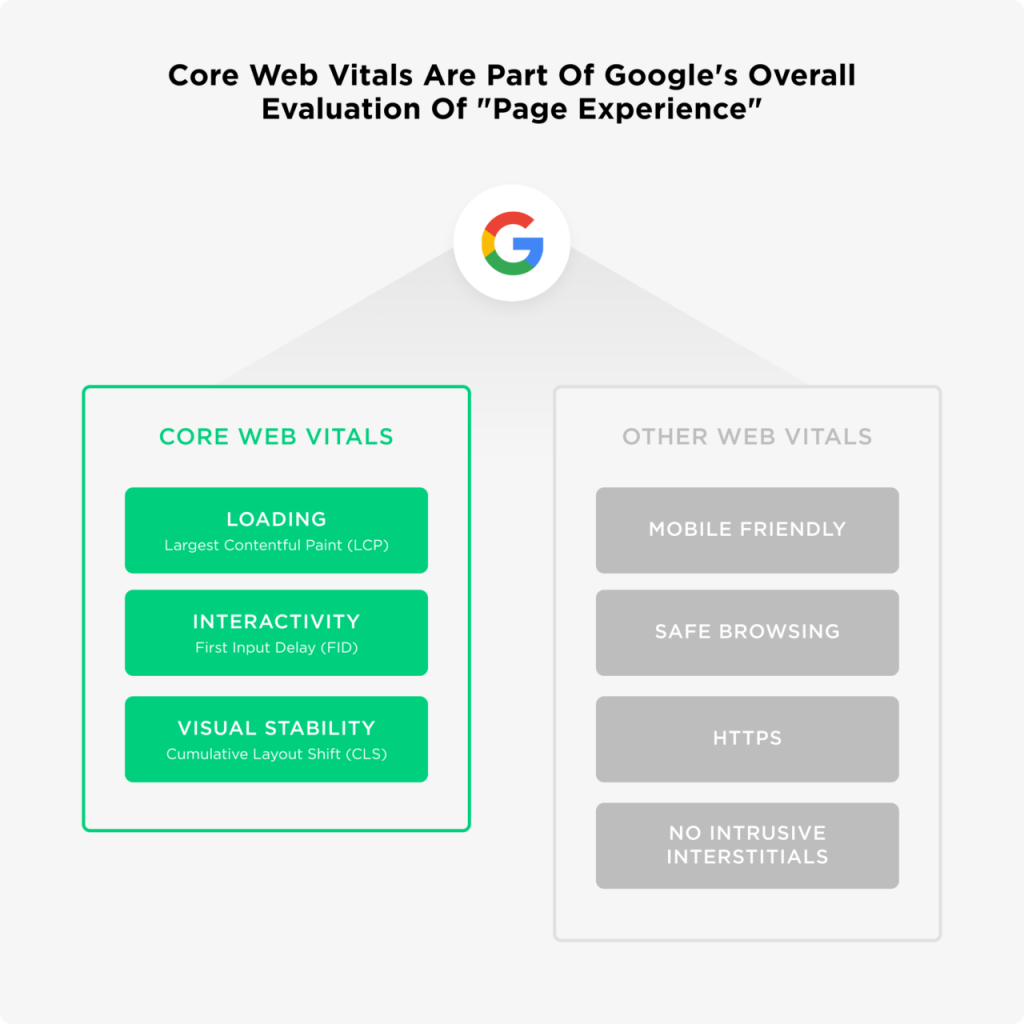
Google had announced in May 2020 that page experience signals would be a part of Google search ranking. These signals would determine if users like the interaction with a web page. One year later, Google is all set to roll out its new metrics for ranking called the Core Web Vitals. They include page experience along with the existing search signals of safe browsing, HTTPS-security and intrusive interstitial guidelines.
What are the latest Google Core Web Vitals?
Google’s Core Web Vitals are real-world experience metrics that Google wants websites to imbibe. These metrics will answer questions like-
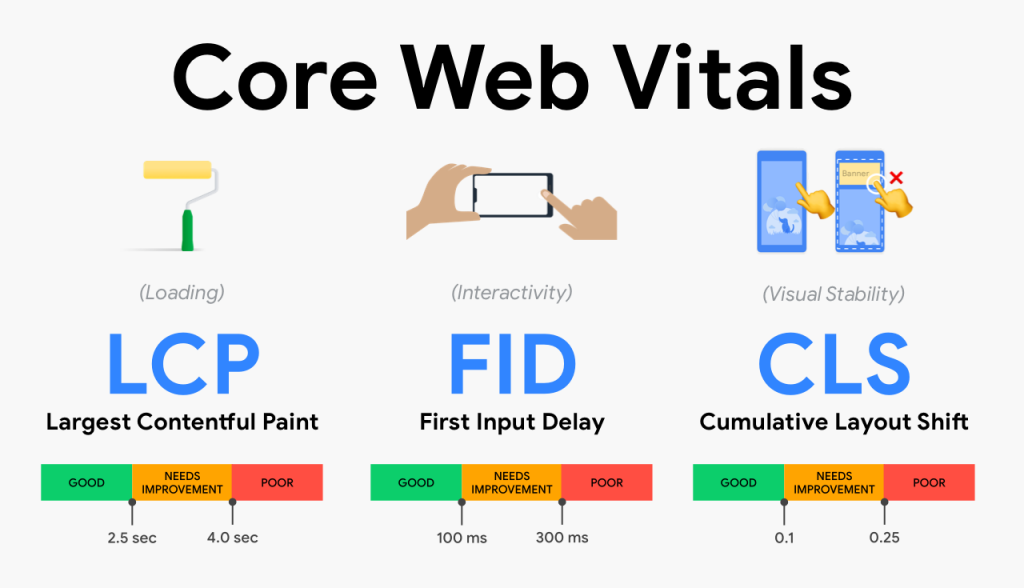
- How fast does the page load? – Largest Contentful Paint
- How fast is it interactive? – First Input Delay
- How fast is it stable? – Cumulative Layout Shift
Basically, these three questions will rate user-experience while visiting a web page from a desktop device or a mobile phone.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
In layman’s term, LCF means the amount of time a web page takes to load completely. A web page is loaded fully when the largest content element of the web page is visible on the page. It could be an image, video or text. If the time taken for the largest element is minimal, the user-interest is retained and he continues his search on that web page. However, if the web page takes a lot of time to load completely, the user might lose interest and go to some other web page. To ensure fast load time keep a watch out for the server response time, CSS, JavaScript, resource load time and client-side rendering. A good score for LCP is less than 2.5 seconds.
- First Input Delay
It is the time taken between a user’s first interaction with the site and the time taken by the browser to actually respond to it. Usually, the first interaction with a site happens when a user clicks a link or taps a button or uses a customized JavaScript-powered control. For instance, if a user clicks on a video link on the web page, how long does it take for the video to start. An ideal measurement is less than 100 milliseconds. If it is anything more than that, Google will understand that your site does not have good interactivity with the user.
Some tactics that could help with FID include:
- Reduce the Javascript execution time
- Decrease the complexity of the website’s main thread
- Cut down on the third-party code running on the site
- Minimize the size and number of file transfers on the site
Remember, first impressions are lasting impressions! FID is all about first impressions because the first time a user interacts with your web page, it becomes the baseline of his experience and gives him an insight into your web performance.
- Cumulative layout shift (CLS)
Have you experienced that while reading an article online, suddenly there are changes on the page? Without any warning, the text moves and you miss where you were on that page? Or sometimes, when you load a page on the mobile phone and click on a button, at the last second, it shifts and you hit some other button altogether or the page layout experiences an unexpected change. This is called layout shift. All this leads to a poor user experience. So now Google has started measuring this user-centric metric and termed it Cumulative layout shift (CLS).
It measures the visual stability of your web page, which essentially means it checks the number of times a user experiences a layout change while browsing a web page. The main reasons for a layout shift are:
- Dynamically injected content
- Images without any dimensions
- Having ads, embeds, and iframes without proportion
- Web fonts that lead to FOIT/FOUT (Flash of Invisible Text and Flash of Unstyled Text)
To fix these issues, you should know the proper size of all the visual media on the website and format them accordingly as per the aspect ratio so that they are properly visible on both desktop and mobile phone. CLS can also be enhanced with reserved ad space, pre-loading web fonts and pre-computing space for embeds.
The lower the CLS, the better is the user experience. To have a good user experience, a website should have a CLS score of less than 0.1.
How will Core Web Vitals affect rankings?
These metrics are going to affect all regular search results both on the mobile and desktop. In fact, these metrics will be critical to be in Google Top Stories, which are the news results that appear on top of all the search results. Earlier, AMP was needed to appear in Google Top Stories, but from May 2021, you will have to meet a basic threshold of the above-mentioned Core Web Vitals.
Conclusion
The main aim of updating Google ranking metrics is to find relevant and quality websites on the web. The latest updates ensure that the users have the best experience and get the information they are looking for without wasting too much time. The Core Web Vitals might seem a little complex but getting a perfect Core Web Vitals score is not an arduous task. Simply follow these pointers and you are sure to go several notches higher in the SERP rankings. However, remember the key to higher ranking is still based on the quality of content and links, so don’t bungle up on those.
Recommended Posts

Elevate Your Digital Presence: A Comprehensive Guide to 2024’s SEO Trends and Predictions
December 13, 2023

Top SEO Trends That Will Rule The SEO World in 2023
January 3, 2023
WhatsApp us


